39 zero coupon bonds definition
What Is Interest Rate Risk? Why Is It Important? - TheStreet Zero-coupon bonds do not offer a coupon payment, and so for this reason they are less affected by interest rate fluctuations. However, if an investor sells their zero-coupon bond prior to its... Learn How I Bonds Work - The Balance This is important because it means that your I bond is really a type of zero-coupon bond. Unlike a traditional corporate bond or municipal bond, you won't receive checks in the mail for the interest you earned. Instead, the value of your I bond will increase regularly. That interest will be added to the principal value.
JOHNSON & JOHNSONLS-NOTES 2007(07/24) Bond - Insider The Johnson & Johnson-Bond has a maturity date of 11/6/2024 and offers a coupon of 5.5000%. The payment of the coupon will take place 1.0 times per Year on the 06.11..
Zero coupon bonds definition
Current Rates | Edward Jones Zero Coupon Bonds These securities are derived from Government of Canada, Provincial Government, and Corporate bonds. The coupons are removed and sold as different securities. The zero coupon security carries the same backing as the original bond. Market and interest risks are greater with zero coupon securities than with the original bond. Treasury Yield Definition - Investopedia While Treasury notes and bonds offer coupon payments to bondholders, the T-bill is similar to a zero-coupon bond that has no interest payments but is issued at a discount to par. An investor... Series I Bond Definition - Investopedia The series I bond is a zero-coupon bond, meaning that no interest is paid during the life of the bond. The interest is, instead, added back to the value of the bond and earns interest on interest....
Zero coupon bonds definition. Pricing risk-based catastrophe bonds for earthquakes at an urban scale ... In case of zero-coupon bond (see Fig. 6 a), we observe that the price of bond decreases with increasing time to maturity. At a given maturity T, the bond price increases with increasing threshold... zero coupon bond - Definition, Understanding, and Why zero coupon bond ... What is Zero Coupon Bond This is an accrual bond that does not pay the interest but trades at a major discount, giving a profit at maturity when the bond is taken out for its total face value. Understanding Zero-Coupon Bonds Some bonds are identified as zero-coupon instruments from the beginning. Accounts That Earn Compounding Interest | The Motley Fool A zero coupon bond holder purchases a bond at a steep discount, receives no interest payments (coupons) in exchange for holding the bond, and is paid the bond's face value when the bond is due. The... Formula, Examples, How to Use RATE Function - Corporate Finance Institute What is the RATE Function? The RATE Function is an Excel Financial function that is used to calculate the interest rate charged on a loan or the rate of return needed to reach a specified amount on an investment over a given period.. For a financial analyst, the RATE function can be useful to calculate the interest rate on zero coupon bonds.. Formula =RATE(nper, pmt, pv, [fv], [type], [guess])
Tax on Long Term Capital Gain under Income Tax Act, 1961 (i) any stock-in-trade (other than securities referred to in (b) above), consumable stores or raw materials held for the purposes of his business or profession ; (ii) personal effects, that is, movable property (including wearing apparel and furniture) held for personal use by the taxpayer or any member of his family dependent on him, but excludes— Cash and Carry Definition & How Does it Work? Cash and Carry Definition. ... The amount paid now can be viewed as a zero-coupon bond since the cost of a box upon its maturity will still be the gap between the strikes engaged. The greater the suggested interest rate, the lesser the box's original cost. 'Synthetic loan' is the term for this notion. How to Invest in Bonds: A Beginner's Guide to Buying Bonds Bonds are a way for an organization to raise money. Let's say your town asks you for a certain investment of money. In exchange, your town promises to pay you back that investment, plus interest,... Accounting for a non interest bearing note — AccountingTools The same approach is used by the issuer of the note, except that interest expense is recorded, and the value of a note payable liability account is gradually increased until such time as the debt is paid off at its face value. Terms Similar to Non Interest Bearing Note A non interest bearing note is also known as a zero-coupon bond. Liabilities
Deferred Coupon Bonds | Definition, How it works? Types, Advantages Zero-Coupon Bonds On this bond, the interest keeps on adding till the maturity of the bond. There is no coupon payment between the issuance date and the maturity date. On maturity, a lump-sum amount is paid to the investor. This is a summation of the principal and the deferred interest. What Are Eurobonds? - The Balance This is when the firm may decide to issue a bond in the U.S. in the form of rupees. The company pays less for the cost of borrowing money. At the same time, U.S. investors gain from a diverse investment. These eurobonds have become more popular with the rise in people doing business around the world. Netherlands Government Bonds - Yields Curve Price Simulation: bonds with a face value of 100, with different coupon rates. The highlighted column refers to the zero coupon bond. Click on for a forecast of the yield. 5 Year Treasury Rate - YCharts The 5 year treasury yield is included on the longer end of the yield curve. Historically, the 5 Year treasury yield reached as high as 16.27% in 1981, as the Federal Reserve was aggressively raising benchmark rates in an effort to contain inflation. 5 Year Treasury Rate is at 3.25%, compared to 3.07% the previous market day and 0.73% last year.
What Is a Zero Coupon Yield Curve? (with picture) A zero coupon bond does not pay interest but instead carries a discount to its face value. The investor therefore receives one payment of the face value of the bond on its maturity. This face value is the equivalent of the principal invested plus interest over the life of the bond.
ICE BofA US High Yield Index Effective Yield - St. Louis Fed Original issue zero coupon bonds, "global" securities (debt issued simultaneously in the eurobond and US domestic bond markets), 144a securities and pay-in-kind securities, including toggle notes, qualify for inclusion in the Index. Callable perpetual securities qualify provided they are at least one year from the first call date.
Quant Bonds - Asset Swap Spread - BetterSolutions.com Uses the Zero Coupon Yield curve. By combining the two you can change the coupon payments to either fixed or floating. This is the yield of the bond minus the swap rate for the corresponding maturity swap. A fixed-rate bond will be combined with an interest rate swap in which the bond holder pays a fixed coupon and receives a floating coupon.
What is Phantom Income? (with picture) - Smart Capital Mind Zero coupon bonds are a common cause of phantom income. They yield no interest to those who possess them, but, because they are sold at a discount, are technically still profitable to their owners and thus taxable.
All the 21 Types of Bonds | General Features and Valuation | eFM A zero-coupon bond is a type of bond with no coupon payments. It is not that there is no yield; the zero-coupon bonds are issued at a price lower than the face value (say 950$) and then pay the face value on maturity ($1000). The difference will be the yield for the investor.
How to Invest in Bonds: A Quick-Start Guide for Beginners The government also issues "zero coupon bonds" that are sold at a discount to their face value and then are redeemable at face value on maturity, but they don't pay any cash interest ...
Amortization of discount on bonds payable - AccountingTools ABC must then reduce the $100,000 discount on its bonds payable by a small amount during each of the accounting periods over which the bonds are outstanding, until the balance in the discount on bonds payable account is zero when the company has to pay back the investors. The bonds have a term of five years, so that is the period over which ABC ...
United States Government Bonds - Yields Curve The United States 10Y Government Bond has a 3.231% yield.. 10 Years vs 2 Years bond spread is 4.6 bp. Yield Curve is flat in Long-Term vs Short-Term Maturities. Central Bank Rate is 1.75% (last modification in June 2022).. The United States credit rating is AA+, according to Standard & Poor's agency.. Current 5-Years Credit Default Swap quotation is 17.00 and implied probability of default is ...
What is a Derivative? | Definition | Simply Explained | Finbold It means either the buyer or the seller can't make the required payments and oblige to the contractual agreement. That is why investors should consider the credit score of each party, as it can usually reflect how high the counterparty risk is before entering the trade.
Series I Bond Definition - Investopedia The series I bond is a zero-coupon bond, meaning that no interest is paid during the life of the bond. The interest is, instead, added back to the value of the bond and earns interest on interest....
Treasury Yield Definition - Investopedia While Treasury notes and bonds offer coupon payments to bondholders, the T-bill is similar to a zero-coupon bond that has no interest payments but is issued at a discount to par. An investor...
Current Rates | Edward Jones Zero Coupon Bonds These securities are derived from Government of Canada, Provincial Government, and Corporate bonds. The coupons are removed and sold as different securities. The zero coupon security carries the same backing as the original bond. Market and interest risks are greater with zero coupon securities than with the original bond.




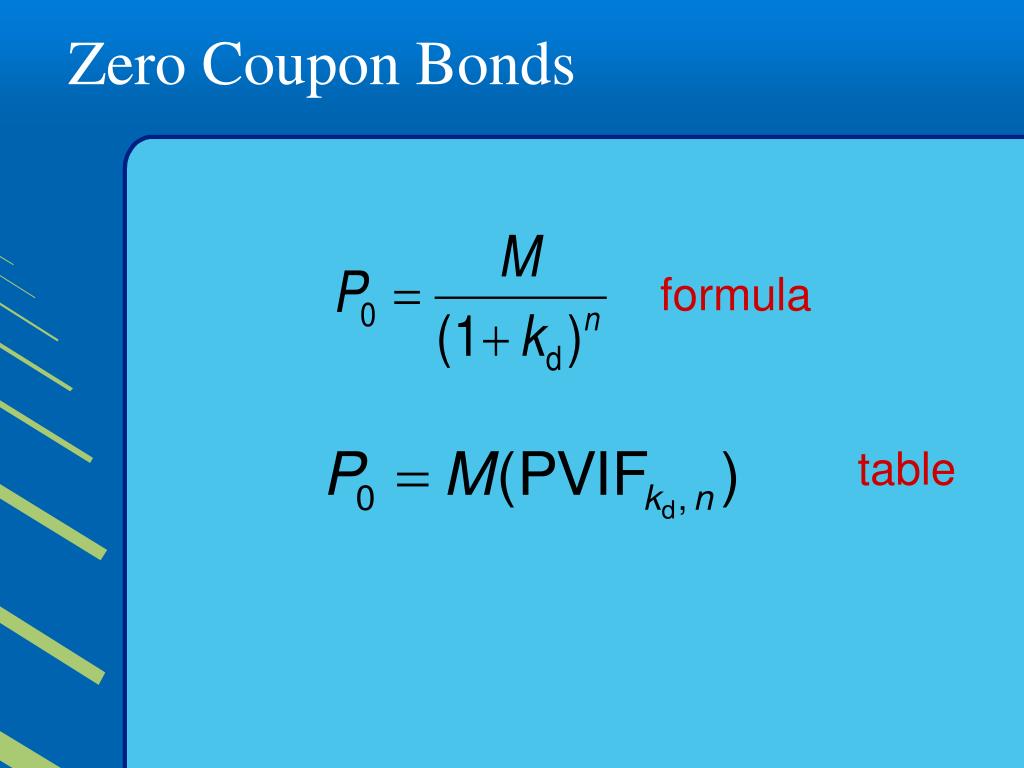

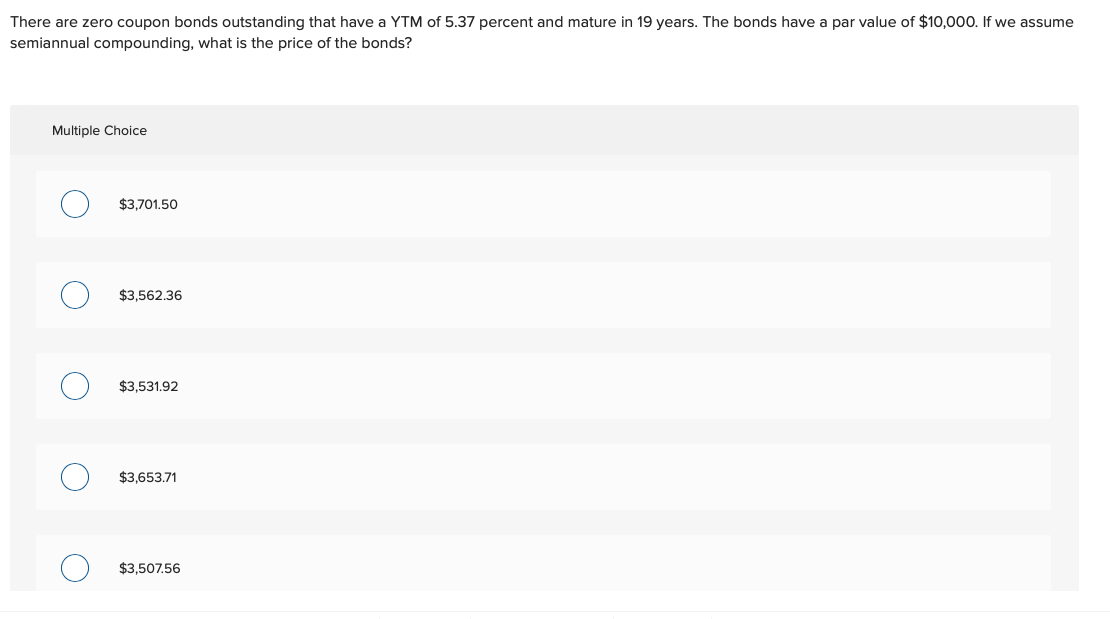
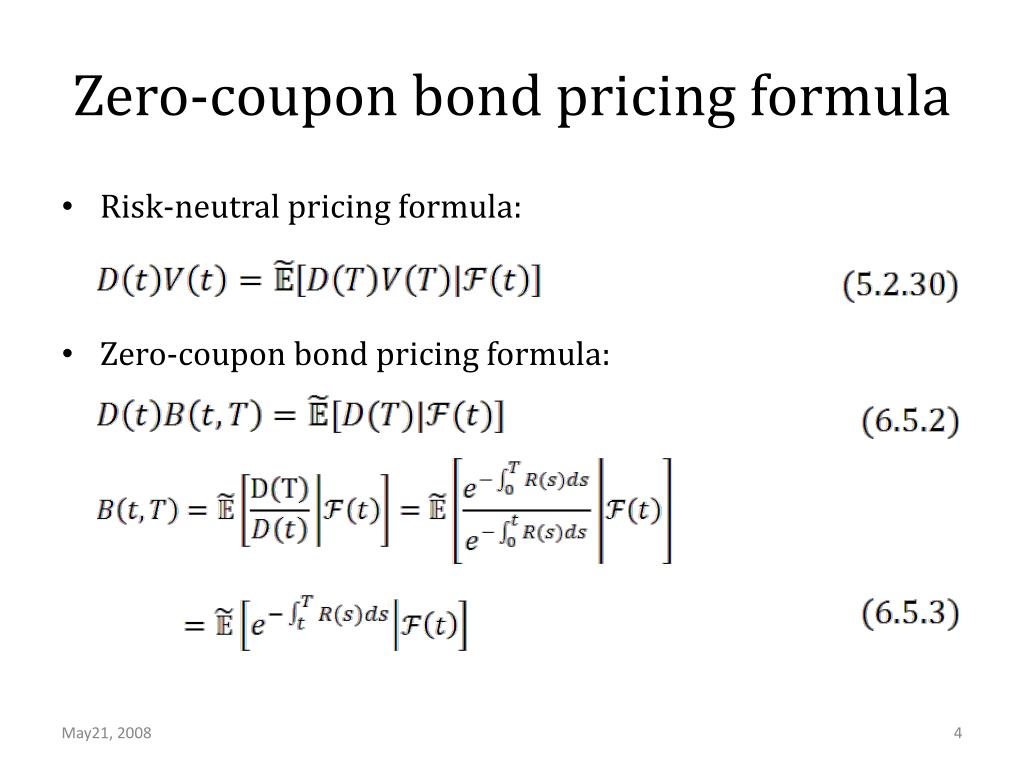


Post a Comment for "39 zero coupon bonds definition"